MGEScan on Amazon Cloud (EC2)¶
With Amazon Cloud Web Services, a virtual single or distributed system for MGEScan can be easily deployed. MGEScan (Amazon machine image ID: ami-10672b7a on ‘US East-Ohio’ region) is available to create our Galaxy-based system for MGEScan which is identifying long terminal repeats (LTR) and non-LTR retroelements in eukaryotic genomic sequences. More cloud options will be available soon including Google Compute Engine, Microsoft Windows Azure or private cloudplatforms such as OpenStack and Eucalyptus.
Note
ami-10672b7a was created in 2015. To apply new updates of MGEScan and Galaxy, follow the instructions below after launching the image on AWS EC2.
- Stop Galaxy server first - processs looks like python ./scripts/paster.py serve universe_wsgi.ini
- Update system packages
sudo yum update -y - Update mgescan code
cd $MGESCAN_SRC;git pull;python setup.py install - Update Galaxy code
cd $GALAXY_HOME;git pull - Migrate Galaxy DB, if necessary
cd $GALAXY_HOME;./run.sh;sh manage_db.sh -c ./universe_wsgi.ini upgrade - Update Galaxy tools
cp -pr $MGESCAN_SRC/galaxy-modified/* $GALAXY_HOME - Start Galaxy server
cd $GALAXY_HOME;nohup bash run.sh &
Command lines only
kill `ps -ef|grep universe_wsgi|grep -v grep|awk '{print $2}'`
sudo yum update -y
cd $MGESCAN_SRC;git pull;python setup.py install
cd $GALAXY_HOME;git pull
cd $GALAXY_HOME;./run.sh;sh manage_db.sh -c ./universe_wsgi.ini upgrade
cp -pr $MGESCAN_SRC/galaxy-modified/* $GALAXY_HOME
cd $GALAXY_HOME;nohup bash run.sh &
Deploying MGEScan on Galaxy¶
First step is getting an Amazon account to launch virtual instances on Amazon IaaS platform EC2.
AWS EC2 Account¶
If you already have an account of Amazon AWS EC2, open AWS Management Console to launch our MGEScan image on EC2. Otherwise, create an AWS Account.
MGEScan Machine Image¶
In AWS Management Console, open EC2 Dashboard > Launch Instance. To choose an Amazon Machine Image (AMI) of MGEScan, select Community AMIs on the left tab, and search by name or id, e.g. mgescan or ami-10672b7a. (US East-Ohio Region Only)
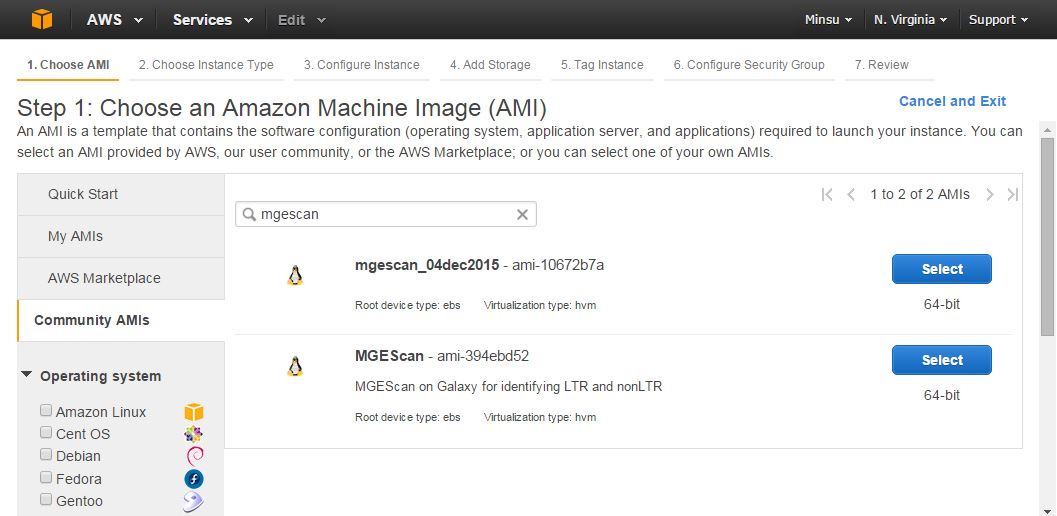
MGEScan EC2 Image Information¶
- Region: US East
- Image Name: MGEScan
- ID: ami-10672b7a
- Server type: 64bit
- Description: MGEscan on Galaxy for identifying LTR and nonLTR
- Root device type: ebs
- Virtualization type: hvm
Choose an Instance Type for MGEScan Instance¶
Once you choose MGEScan image as a base image, you need to select the size
of instance. t2.micro uses 1 vCPUs and 1 GB memory which is in free tier.
Ohter options are available to have large instance e.g. 40 vCPUs. Click
Review and Launch icon at bottom of the page.
Tip
t2.micro: (Variable ECUs, 1 vCPUs, 2.5 GHz, Intel Xeon Family, 1 GiB memory, EBS only)
Security Group for Web¶
MGEscan / Galaxy uses 38080 default web port. We need to add a rule to have
this port opened on the new instance.
There are a few steps you have to follow.
- Find “Security Groups” section and click “Edit security groups”. “Create a new
security group” is selected as a default with a 22 SSH port opened to anywhere.
- We will add
38080tcp port. Click “Add Rule” and type38080in the “Port Range” input box. - Don’t forget to update “Source” to “Anywhere” from “Custom IP”.
- Once you’re done, click “Reivew and Launch”.
- Click “Launch” again.
- Choose a SSH keypair from existing or new one.
- Click “Launch Instance” and wait.
- Find out public IP address and open a web browser with the address. e.g. http://[IP address]:38080 Don’t forget the port number 38080
Access to MGEScan Instance¶
Once the MGEScan instance is launched and accessible, galaxy scientific workflow system for MGEScan and SSH connection are avabilable through given dns name.
Ready To Use¶
The MGEScan is now ready to conduct your experiment on Amazon EC2.
Note
Do not forget to terminate your virtual instance after all analysis completed. Amazon Cloud charges use of VM instances hourly.
Terminating AWS Instance:
Note¶
Add a script to auto-start Galaxy after reboot in /etc/rc.local
su ec2-user -c 'source ~/.mgescanrc;cd $GALAXY_HOME;nohup sh run.sh &'