MGEScan-LTR¶
MGEScan-LTR program identifies long terminal repeats (LTR). RepeatMasker can be used to identify repetitive elements in genomic sequences.
Description¶
MGEScan-LTR identifies all types of LTR retrotransposons, i.e., young intact, old intact, and solo LTR retrotransposons, without relying on a library of known elements. It uses approximate string matching, protein domain analysis, and profile Hidden Markov Models to identify intact LTR retrotransposons.
For details, please read following references.
- Rho, M., et al. (2007) De novo identification of LTR retrotransposons in eukaryotic genomes. BMC Genomics, 8, 90.
- Rho, M., et al. (2010) LTR retroelements in the genome of Daphnia pulex. BMC Genomics, 11, 425.
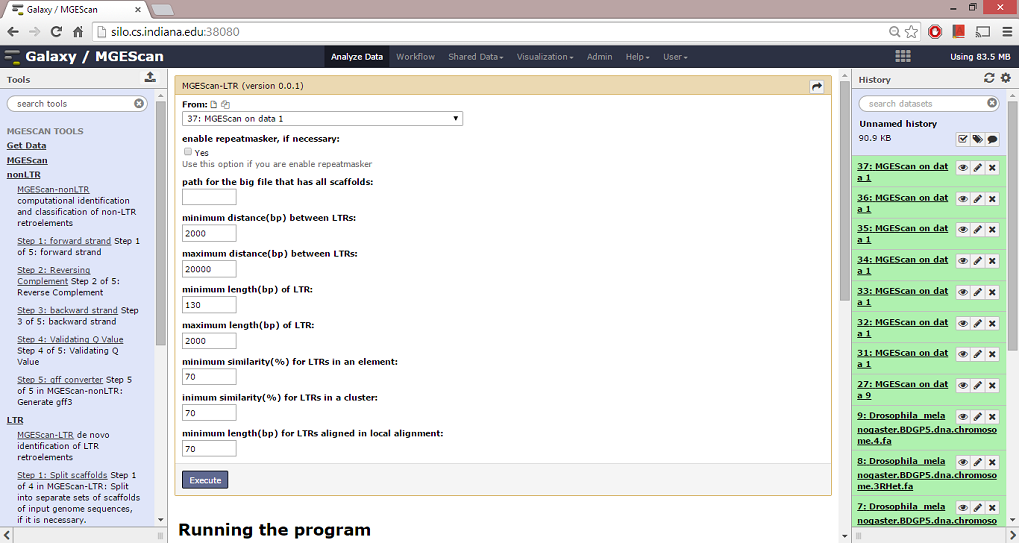
Running the program¶
To run MGEScan-LTR, follow the steps below,
- Specify options that you like to have:
- Check repeatmasker if you want to preprocess
- Check scaffold if the input file has all scaffolds.
- Update values:
- min_dist: minimum distance(bp) between LTRs.
- max_dist: maximum distance(bp) between LTRS
- min_len_ltr: minimum length(bp) of LTR.
- max_len_ltr: maximum length(bp) of LTR.
- ltr_sim_condition: minimum similarity(%) for LTRs in an element.
- cluster_sim_condition: minimum similarity(%) for LTRs in a cluster
- len_condition: minimum length(bp) for LTRs aligned in local alignment.
- Click ‘Execute’
Options¶
- RepeatMasker: Yes / No
- file path for multiple sequences to divide
- settings for LTRs
- minimum distance(bp) between LTRs
- maximum distance(bp) between LTRs
- minimum length(bp) of LTR
- maximum length(bp) of LTR
- minimum similarity(%) for LTRs in an element
- minimum similarity(%) for LTRs in a cluster
- minimum length(bp) for LTRs aligned in local alignment
Results¶
Upon completion, MGEScan-LTR generates a file ltr.out. This output file has information about clusters and coordinates of LTR retrotransposons identified. Each cluster of LTR retrotransposons starts with the head line of [cluster_number]———, followed by the information of LTR retrotransposons in the cluster. The columns for LTR retrotransposons are as follows.
- LTR_id: unique id of LTRs identified. It consist of two components, sequence file name and id in the file. For example, chr1_2 is the second LTR retrotransposon in the chr1 file.
- start position of 5 LTR.
- end position of 5 LTR.
- start position of 3 LTR.
- end position of 3 LTR.
- strand: + or -.
- length of 5 LTR.
- length of 3 LTR.
- length of the LTR retrotransposon.
- TSD on the left side of the LTR retotransposons.
- TSD on the right side of the LTR retrotransposons.
- di(tri)nucleotide on the left side of 5LTR
- di(tri)nucleotide on the right side of 5LTR
- di(tri)nucleotide on the left side of 3LTR
- di(tri)nucleotide on the right side of 3LTR
License¶
Copyright 2015. You may redistribute this software under the terms of the GNU General Public License.